Hepatitis C and the liver
- Medically reviewed by
- AKF's Medical Advisory Committee
- Last updated
- March 28, 2022
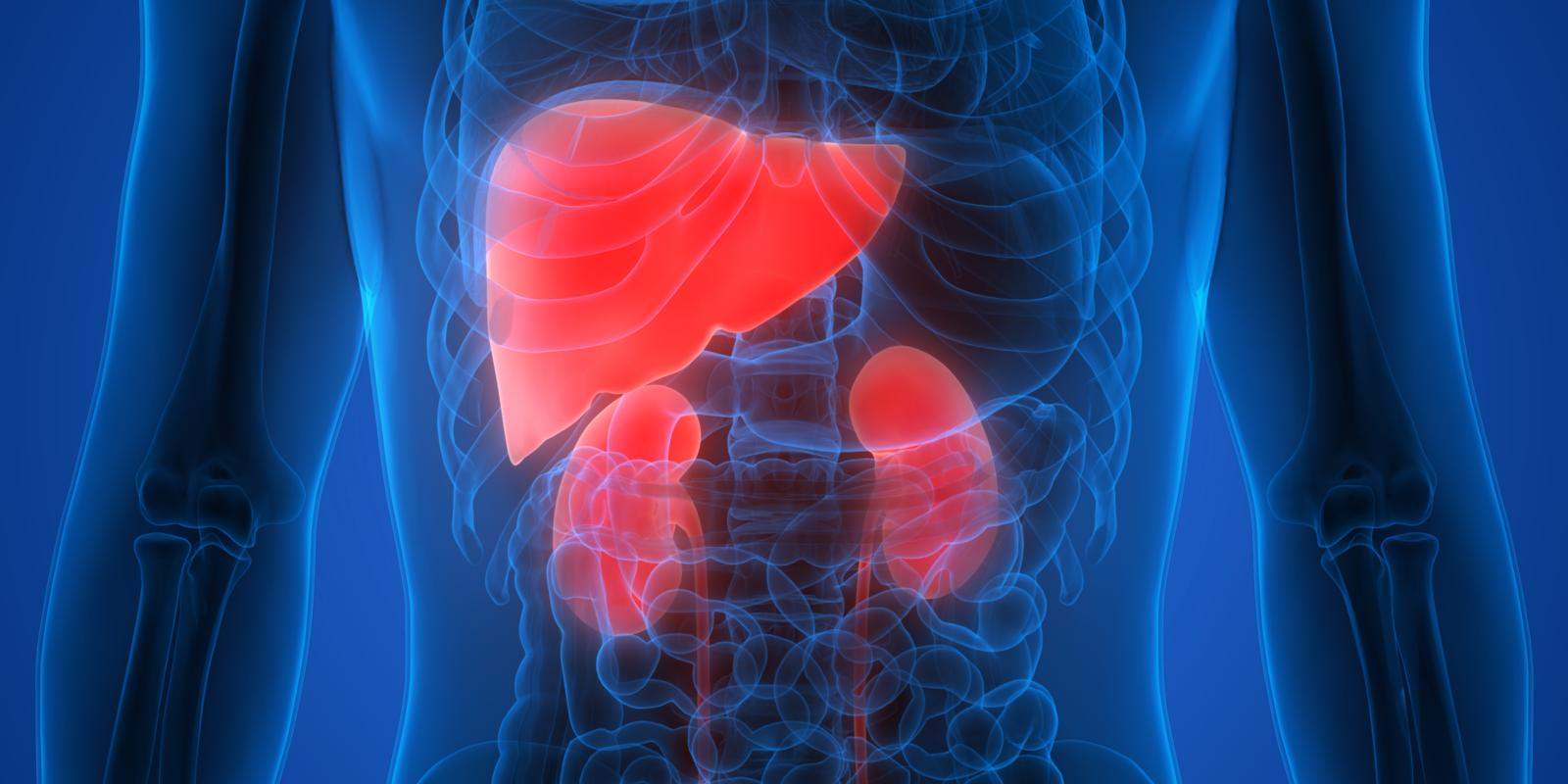
Your liver is a very important organ in the body. The most important jobs of your liver are to:
- Control the levels of healthy and unhealthy chemicals in your body. When you eat or drink, you take in nutrients (like protein, carbohydrates and fats). Your liver turns these nutrients into a form that your body can take in.
- Break down toxins (harmful substances), like drugs or alcohol. It either turns the toxins into something safe for your body, or it makes sure the toxins are removed from your body.
Your liver also:
- Helps with blood clotting
- Helps get rid of old or damaged blood cells
- Helps get rid of certain fats and take in others
- Helps control your blood sugar
- Helps make cholesterol
- Helps your body fight infection
Hepatitis C and the liver
Hepatitis C is a disease that attacks the liver. It is caused by the hepatitis C virus, which is spread by coming into contact with the blood of a person infected with hepatitis C. The hepatitis C infection can be acute (happen right away) or be chronic (ongoing).
- An acute hepatitis C infection usually happens in the first six months of being infected with the virus. Most of the time, acute hepatitis C infection will lead to chronic hepatitis C infection. Acute hepatitis C usually has no symptoms.
- A chronic hepatitis C infection happens when the virus stays in your body for a long period of time. You can have chronic hepatitis C for many years without realizing it. Chronic hepatitis C can sometimes lead to serious liver damage or even death.
Hepatitis C causes the liver to become inflamed (swollen), which can affect the body's ability to work properly. If not treated, this disease can cause permanent damage to your liver, and can lead to liver cancer or liver failure. This is why it is important to be tested and treated early for hepatitis C to prevent or delay serious liver damage.